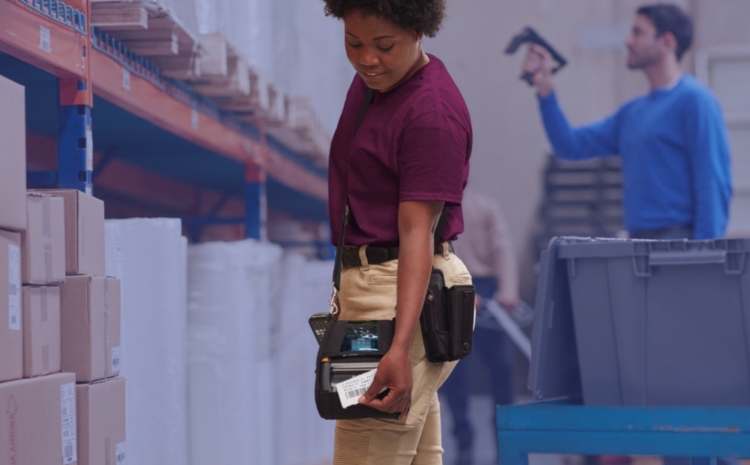
Selecting the right label supply for your business is about ensuring operations run smoothly, products are tracked accurately, and customers receive reliable information. Labels are everywhere, yet its importance often goes unnoticed until something goes wrong. MultiSystems, with decades of expertise, provides a range of advanced label solutions that cater to all businesses. Partnering with Zebra Technologies, MultiSystems ensures you get precision-engineered labels designed to meet the toughest industry challenges.
Product identification labels are a crucial mechanism for maintaining operational efficiency. They form the final link between your company and the key stakeholders for your product, including customers, healthcare providers, patients, and regulators.
Although thousands of thermal label types exist, they’re certainly not all the same. Each label material has different attributes that make it suitable for specific environments or applications. It is critical that the labels you use remain legible and scannable not only when they leave the warehouse, but also throughout their entire lifecycle and at the time of disposal. To help you make informed decisions, lets explore the fundamental principles of thermal printing, the key factors to consider when selecting label materials, and what to look for in a label supplier.
Understanding Thermal Printing Basics: Direct Thermal vs. Thermal Transfer

When it comes to label printing, thermal printing technologies are a top choice for businesses of all sizes due to their speed, reliability, and ability to produce high-quality, scannable labels. Whether used for shipping, product identification, or compliance labeling, thermal printing ensures consistent performance across various industries. However, the two primary thermal printing methods—direct thermal and thermal transfer—operate differently and are best suited for specific applications. Understanding these differences is essential to selecting the right equipment and materials for your needs.
Direct Thermal Printing
Direct thermal printing utilizes heat-sensitive media coated with a chemical layer that darkens upon contact with the heated printhead. Since the printhead directly interacts with the label, no ribbon is needed, the image (text, barcodes, or graphics) is formed as the label’s surface reacts to the applied heat.
Durability
Direct thermal printing delivers sharp, high-contrast images that are easy to scan and read. Barcodes and text typically print crisply, making them ideal for short-term identification needs. Over extended periods or in conditions where labels might rub against surfaces, the print can begin to degrade.
Print Quality
Direct thermal printing delivers sharp, high-contrast images that are easy to scan and read. Barcodes and text typically print crisply, making them ideal for short-term identification needs. Over extended periods or in conditions where labels might rub against surfaces, the print can begin to degrade.
Application Environment:
Direct thermal printing excels in controlled indoor settings where extreme temperatures, moisture, and chemical exposure are minimal. They’re also a strong choice when quick, on-demand printing is required, think retail stores, small warehouses, or businesses with rapid turnaround.
Common Uses
Shipping Labels: short transit time, low environmental stress
Retail Price Tags: often replaced frequently
Event Tickets: used for a limited duration
Patient Wristbands: hospital or clinical environments where labels are used briefly
Short-Life Product Labels: items with quick turnover or limited shelf life
Thermal Transfer Printing
Thermal transfer printing uses a heated ribbon to deposit ink onto a label. As the printhead applies heat, the ink on the ribbon melts or vaporizes and bonds to the label surface. This method involves three primary components: the printer, a specialized ribbon (wax, wax/resin, or resin), and the label media.
Durability
Thermal transfer labels are known for their resilience. The ink transferred from the ribbon creates a more stable image that can endure challenging environments, including exposure to heat, abrasion, and certain chemicals. This added toughness makes thermal transfer an excellent option for labels that must remain readable for longer periods or in demanding conditions.
Print Quality
Crisp, long-lasting text and barcodes are hallmarks of thermal transfer printing. Since the ink bonds to the label surface, the final result is often more durable and resistant to fading. This print stability is especially beneficial for applications requiring reliable scanning from production to end-of-life.
Application Environment
Thermal transfer printing is widely used in industrial, laboratory, and outdoor environments where labels may be subjected to tough conditions. For instance, chemical processing plants, manufacturing floors, and high-heat scenarios benefit from the durability thermal transfer provides. Label longevity is a key advantage, making this technology ideal for any application where readability must be maintained over months or years
Common Uses
Asset Tracking: long-term identification of equipment or parts
Laboratory Samples: withstand cold storage, chemicals, handling
Chemical Drum Labels: resistant to harsh substances and UV exposure
Automotive Parts Labeling: durable for parts under stress
Long-Term Product Identification: products stored in warehouses or exposed to fluctuating condition
By considering each technology’s durability, print quality, application environment, and typical use cases, businesses can pinpoint whether direct thermal or thermal transfer printing is the best fit. Direct thermal printing shines in short-life applications with minimal environmental stress, while thermal transfer printing offers superior resilience for labels that must withstand harsh conditions or extended lifespans.
Ribbon, Liner, Ink and Media

Direct thermal printing forgoes ribbons altogether, but thermal transfer relies on the extra layer to create indelible prints. Below, we break down the essentials you need to know about ribbons, liner, inks, media, and how they work together.
In thermal transfer printing, the ribbon is the vehicle that carries the ink. When heat is applied via the printhead, the ink either melts or vaporizes, transferring onto the label’s surface. The composition of this ribbon ink varies, and each type is designed to meet different performance requirements.
- Wax Ribbons: Are an economical option designed primarily for printing on standard paper labels. By melting at relatively low temperatures, they produce crisp, clear images but may smudge or fade under high heat, friction, or chemical exposure. This makes them most suitable for short-term labeling needs, such as shipping or retail tags, where minimal environmental stress is expected.
- Wax/Resin: Ribbons strike a balance between cost and durability by combining wax with resin. The result is greater scratch and chemical resistance than pure wax ribbons, making them a reliable choice for products stored or handled in mildly demanding settings. These ribbons work well on both paper and some synthetic labels. Offering clear prints that hold up better than wax-only options.
- Resin Ribbons: deliver the highest level of durability and are ideal for harsh environments involving significant heat, chemicals, or abrasion. Formulated with resin-based ink, these ribbons bond more firmly to synthetic label materials (like polyester or polypropylene), producing long-lasting images that resist fading or smearing. Although they come at a higher price point, resin ribbons are indispensable for industries that require consistent label readability over extended periods or in extreme conditions.
How Ink and Media Interact

The success of thermal transfer printing largely depends on a compatible match between the ribbon and the label media. Labels generally consist of a face stock (paper or synthetic), an adhesive layer, and a liner backing (discussed below). Each type of face stock has unique surface properties that interact differently with various ink formulations.
- Paper Labels: Often paired with wax or wax/resin ribbons, paper labels are cost-effective for everyday applications like shipping, shelving, or general product labeling.
- Synthetic Labels: Made from materials like polypropylene, polyester, or vinyl, these labels offer greater durability, water resistance, and tear resistance. Resin or wax/resin ribbons are usually recommended, depending on the specific durability demands and environmental conditions.
A balanced ink-media combination ensures optimal print quality and durability. If the ribbon is not well-suited to the face stock, you may encounter issues like poor print quality, fading, smudging, or reduced barcode scan rates.
Linered Labels VS Linerless Labels
Linered
Are a more traditional option, where the labels are attached to a backing sheet. These labels come in predefined sizes, which means you must carefully select the size that fits your specific needs and ensure compatibility with your printer. Depending on your printing equipment, you will need to determine if it supports standard tear, peel-and-present, or cutter functionality.
While liners offer stability and consistency during printing, they come with limitations. Each roll is dedicated to a specific size, meaning any changes in your labeling requirements might require switching rolls, which can increase downtime. Additionally, the liner becomes waste after use, leading to higher material disposal volumes unless a recycling program is implemented.
Linerless
Linerless labels, on the other hand, eliminate the need for a backing altogether. Instead of relying on a release liner, the labels use a special adhesive coating that prevents sticking before application. This provides several operational advantages:
- Enhanced Printer Requirements: To use linerless labels, you need a printer equipped with a cutter mechanism. Unlike traditional printers, these specialized printers can accurately cut the label to your desired size after printing.
- Multiple Label Sizes per Roll: Linerless labels allow you to print varying label sizes from the same roll. This flexibility means you can adapt to changing needs without having to swap rolls, reducing printer downtime and increasing efficiency.
- Sustainability Benefits: By eliminating the liner, linerless labels reduce waste entirely. This not only cuts disposal costs but also aligns with sustainability initiatives by reducing environmental impact.
Key Factors to Consider in Label Selection

Environmental Conditions
Labels often face challenging environments, with factors such as temperature, humidity, chemical exposure, and UV light that can affect print clarity and adhesive strength. Extreme heat can cause labels to curl or inks to fade, while cold or damp conditions may compromise adhesion if the label isn’t designed for those temperatures. In chemical or industrial settings, exposure to solvents or abrasive surfaces can rapidly wear down label materials. And if your products are frequently exposed to direct sunlight, UV-resistant labels are essential for preventing discoloration and maintaining legibility. By selecting a label material and adhesive tailored to the expected environment, you can help ensure the information on your labels remains readable from production to end-of-life.
Application Requirements
It’s very important to consider how and where labels will be used. For some products, you might need a permanent adhesive that withstands handling, shipping, or storage without peeling. Other scenarios, like temporary promotions or reusable containers may call for removable adhesives that won’t damage surfaces when removed. Think about the surfaces your labels will adhere to as well: curved bottles, plastic containers, or corrugated cardboard boxes each present different bonding challenges. Additionally, consider the intended lifecycle of the label. Will it need to be legible for a few weeks, or will it face years of wear and tear? Understanding these variables will help you choose a label that performs reliably throughout its intended lifespan.
Industry Compliance and Regulations
Many industries, such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing, have strict labeling requirements. Non-compliance can lead to legal penalties, product recalls, or reputational damage. It’s crucial to stay up to date on relevant regulations and select label materials and designs that meet these standards, from chemical-resistant inks to specific hazard symbols and wording. This not only protects your business from legal risks but also fosters trust with customers and partners who rely on accurate, compliant product information.
Label Technologies and Their Applications
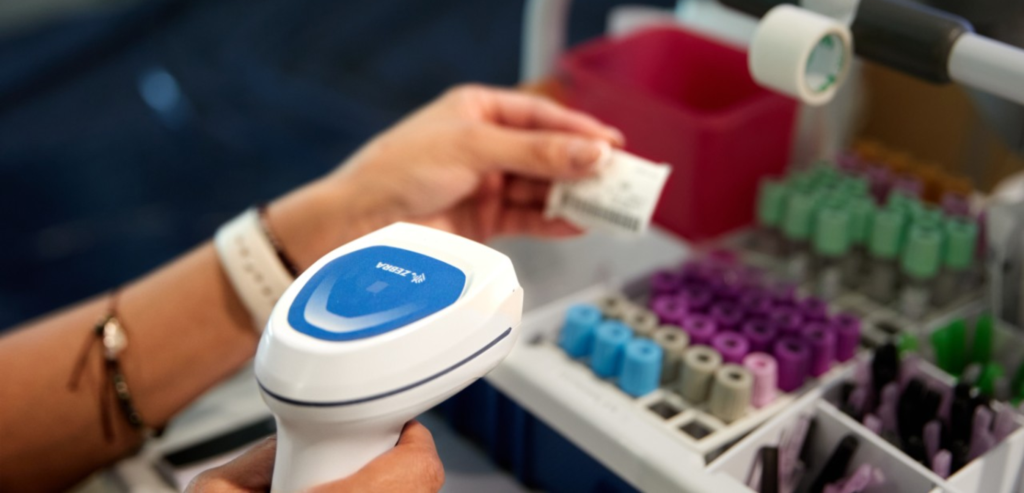
Barcode Labels: Barcodes remain one of the most prevalent labeling technologies worldwide. They store product or track data in a machine-readable pattern, making them easy to scan with standard readers. Commonly used for inventory management, retail, and logistics, barcodes are cost-effective and simple to integrate with most systems. This straightforward approach to data capture is ideal for businesses looking to streamline operations without investing in more complex solutions.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification): Labels utilize radio waves to transmit information between a tag and a reader. Unlike barcodes, they do not require a direct line of sight, enabling quick, bulk scanning. This feature is particularly valuable in warehouse logistics, asset tracking, and event management. Where high volumes of goods or participants move rapidly. By eliminating the need to scan each item individually, RFID cuts down on labor costs and improves operational efficiency.
QR Codes: (Quick Response) codes are two-dimensional barcodes capable of storing a large amount of data. Easily scanned by smartphones, they bridge the gap between physical products and digital information. This makes QR codes an excellent choice for marketing campaigns, product authentication, and user manuals. For example, a cosmetics brand might print QR codes on its packaging to give customers instant access to tutorials, reviews, or ingredient details—providing an interactive, value-added experience.
Choosing the Right Supplier

Choosing the right label supplier is just as crucial as selecting the materials themselves. Look for a partner that truly understands your industry’s needs. Whether that involves strict regulations, demanding environmental conditions, or brand-focused designs. At MultiSystems, for example, we pride ourselves on offering both expertise and flexibility, providing a wide range of adhesives, printing methods, and customization options. This ensures that, if off-the-shelf solutions don’t quite fit, you can still develop a tailored label strategy that aligns perfectly with your operational goals and brand image.
Quality assurance is another important factor. MultiSystems follows rigorous internal testing protocols and best practices. Ensures industry leaders that our products meet or exceed performance standards. This includes evaluating how labels hold up under various temperatures, moisture levels, and chemical exposures, as well as verifying barcode readability over time. Beyond adhering to these strict quality measures, a reliable supplier should also offer outstanding customer service and technical support. Knowing you can rely on knowledgeable professionals to swiftly address printing issues, help you select the right materials, or tailor solutions to your environment brings peace of mind and reduces costly downtime.
Once you finalize your choice, establish clear Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) and train your team on label application, handling, and storage. By regularly monitoring label performance and making necessary adjustments to materials or processes, you’ll ensure that your labels remain both compliant and visually consistent throughout their lifecycle, protecting your brand and streamlining your supply chain in the process.
Conclusion
Choosing the right label solution goes beyond selecting between direct thermal and thermal transfer printing. Factors such as environmental conditions, compliance standards, branding requirements, and supplier expertise all play a critical role in ensuring your labels meet both operational and strategic objectives. By thoroughly evaluating your labeling needs and partnering with experienced industry professionals like MultiSystems, you can optimize efficiency, ensure compliance, and enhance your brand’s integrity across every stage of the supply chain.